View, Transform and Warp
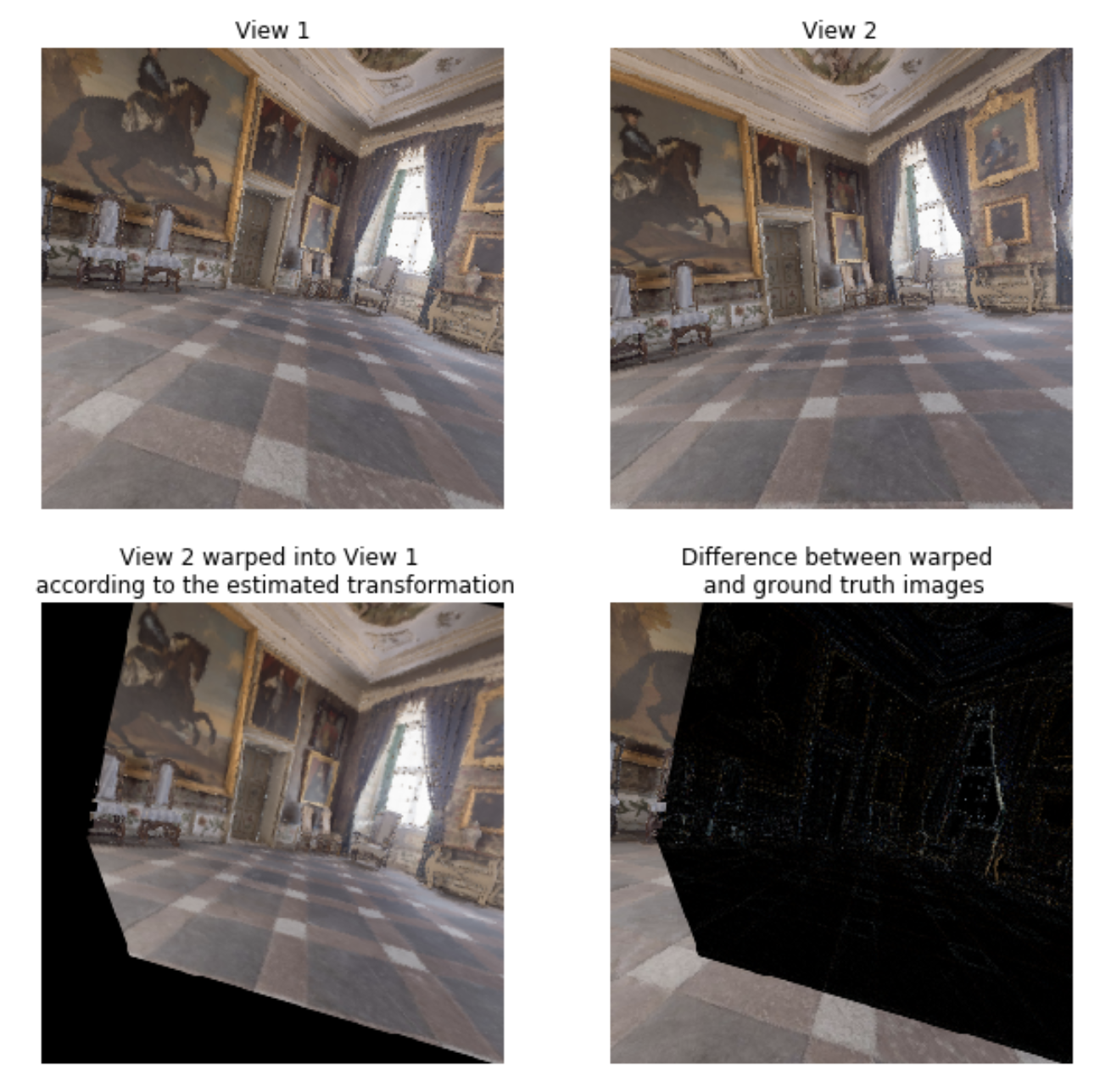
Demonstrates how to extract camera parameters in the scene and how these camera parameters relate to the given views. We create 2 cameras and use RGB and Depth information to construct transformation from a view of camera 1 to camera 2 and validate that transformation comparing projected and original views.
import os import numpy as np import quaternion import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import habitat from habitat.config import read_write from habitat.config.default import get_agent_config import torch.nn.functional as F import torch from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor # Set up the environment for testing config = habitat.get_config(config_paths="benchmark/nav/pointnav/pointnav_habitat_test.yaml") with read_write(config): config.habitat.dataset.split = "val" agent_config = get_agent_config(sim_config=config.habitat.simulator) agent_config.sim_sensors.depth_sensor.normalize_depth = False # Intrinsic parameters, assuming width matches height. Requires a simple refactor otherwise W = agent_config.sim_sensors.depth_sensor.width H = agent_config.sim_sensors.depth_sensor.height assert(W == H) hfov = float(agent_config.sim_sensors.depth_sensor.hfov) * np.pi / 180. env = habitat.Env(config=config) obs = env.reset() initial_state = env._sim.get_agent_state(0) init_translation = initial_state.position init_rotation = initial_state.rotation
2019-06-11 10:03:34,049 initializing sim Sim-v0 I0611 10:03:34.056092 64715 simulator.py:78] Loaded navmesh ../data/scene_datasets/habitat-test-scenes/skokloster-castle.navmesh 2019-06-11 10:03:35,053 initializing task Nav-v0
Randomly permute the rotation
def uniform_quat(original_angle): original_euler = quaternion.as_euler_angles(original_angle) euler_angles = np.array([(np.random.rand() - 0.5) * np.pi / 9. + original_euler[0], (np.random.rand() - 0.5) * np.pi / 9. + original_euler[1], (np.random.rand() - 0.5) * np.pi / 9. + original_euler[2]]) quaternions = quaternion.from_euler_angles(euler_angles) return quaternions
Generate two random, overlapping views
depths = [] rgbs = [] cameras = [] for i in range(0, 2): rotation = uniform_quat(init_rotation) translation = init_translation + np.random.rand(3,) * 0.5 - 0.25 obs = env._sim.get_observations_at(position=translation, rotation=rotation, keep_agent_at_new_pose=True) depths += [obs["depth"][...,0]] rgbs += [obs["rgb"]] cameras += [env._sim.get_agent_state()] env.close()
Intrinsic parameters, K
K = np.array([ [1 / np.tan(hfov / 2.), 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1 / np.tan(hfov / 2.), 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1, 0], [0., 0., 0, 1]]) # Now get an approximation for the true world coordinates -- see if they make sense # [-1, 1] for x and [1, -1] for y as array indexing is y-down while world is y-up xs, ys = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-1,1,W), np.linspace(1,-1,W)) depth = depths[0].reshape(1,W,W) xs = xs.reshape(1,W,W) ys = ys.reshape(1,W,W) # Unproject # negate depth as the camera looks along -Z xys = np.vstack((xs * depth , ys * depth, -depth, np.ones(depth.shape))) xys = xys.reshape(4, -1) xy_c0 = np.matmul(np.linalg.inv(K), xys) # Now load in the cameras, are in the format camera --> world # Camera 1: quaternion_0 = cameras[0].sensor_states['depth'].rotation translation_0 = cameras[0].sensor_states['depth'].position rotation_0 = quaternion.as_rotation_matrix(quaternion_0) T_world_camera0 = np.eye(4) T_world_camera0[0:3,0:3] = rotation_0 T_world_camera0[0:3,3] = translation_0 # Camera 2: translation_1 = cameras[1].sensor_states['depth'].position quaternion_1 = cameras[1].sensor_states['depth'].rotation rotation_1 = quaternion.as_rotation_matrix(quaternion_1) T_world_camera1 = np.eye(4) T_world_camera1[0:3,0:3] = rotation_1 T_world_camera1[0:3,3] = translation_1 # Invert to get world --> camera T_camera1_world = np.linalg.inv(T_world_camera1) # Transformation matrix between views # Aka the position of camera0 in camera1's coordinate frame T_camera1_camera0 = np.matmul(T_camera1_world, T_world_camera0) # Finally transform actual points xy_c1 = np.matmul(T_camera1_camera0, xy_c0) xy_newimg = np.matmul(K, xy_c1) # Normalize by negative depth xys_newimg = xy_newimg[0:2,:] / -xy_newimg[2:3,:] # Flip back to y-down to match array indexing xys_newimg[1] *= -1
And visualise this new transformation
# Create sampler sampler = torch.Tensor(xys_newimg).view(2, W, W).permute(1,2,0).unsqueeze(0) # Create generated image img1_tensor = ToTensor()(rgbs[0]).unsqueeze(0) img2_tensor = ToTensor()(rgbs[1]).unsqueeze(0) img2_warped = F.grid_sample(img2_tensor, sampler) # Visualise plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) ax1 = plt.subplot(221) ax1.imshow(img1_tensor.squeeze().permute(1,2,0)) ax1.set_title("View 1", fontsize='large') ax1.axis('off') ax1 = plt.subplot(222) ax1.imshow(img2_tensor.squeeze().permute(1,2,0)) ax1.set_title("View 2", fontsize='large') ax1.axis('off') ax1 = plt.subplot(223) plt.imshow(img2_warped.squeeze().permute(1,2,0)) ax1.set_title("View 2 warped into View 1 \n according to the estimated transformation", fontsize='large') ax1.axis('off') ax1 = plt.subplot(224) ax1.imshow(np.abs(img2_warped.squeeze().permute(1,2,0) - img1_tensor.squeeze().permute(1,2,0))) ax1.set_title("Difference between warped \n and ground truth images", fontsize='large') ax1.axis('off') plt.show()
(-0.5, 255.5, 255.5, -0.5)